Uniballs and spherical bearings

Information about uniballs / rod ends / ball joints, spherical bearings and accessories.
- What are uniballs?
- Different types
- Uniball size
- Material
- Install uniballs
- Accessories
- Common problems
- Compare uniballs
1 ▼
What are uniballs?
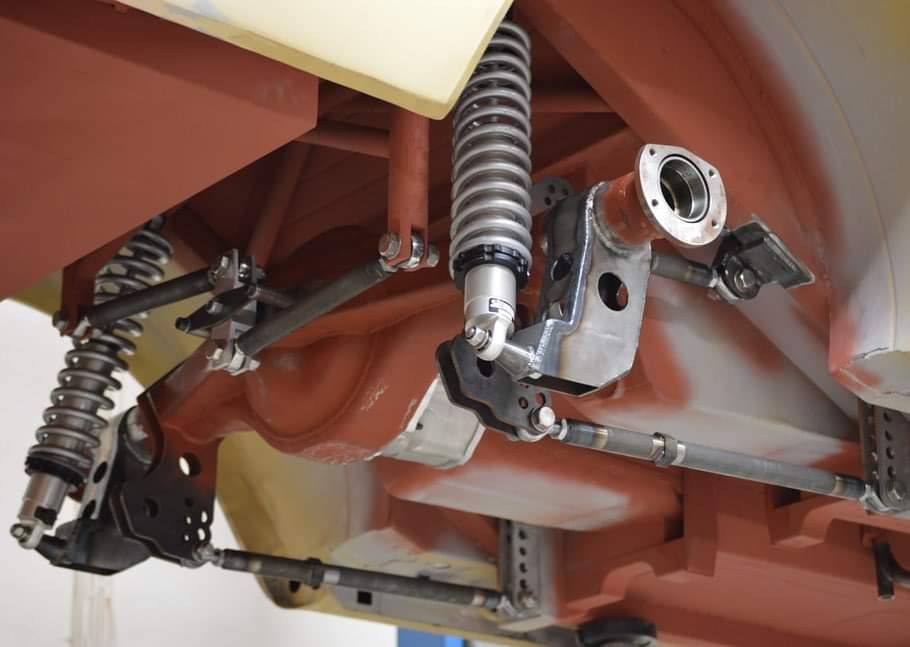
A rod end / Uniball, often used in a motorsport context, is a spherical bearing that is fitted with an external thread or an internal thread. Also available for welding. These components are used in joints instead of a bushing because these do not flex. In motorsport, these are used to get a responsive chassis as you avoid the flex from all bushings.Used where you have a movement and you want a flexible joint and at the same time have the possibility of adjustment. For example, with rear suspension. In motorsport, adjustability is important as you can easily adjust a uniball joint without dismantling.
Since Uniballs are manufactured to withstand tougher loads and have wide tolerances, it facilitates a relatively simple and flexible assembly and at the same time has a good service life.
2 ▼
Different types
There are many different types of joint bearings and rod ends depending on the application and it is important to choose the right one in order not to wear out the part prematurely and that the function fails.
The ball bearings / uniballs found in motorsport have a self-lubricating (oily) plastic bearing that allows the ball to move easily. Industry has greasable ball bearings, this is not used in motorsport. These must be continuously greased to be free of play.
- Female Rod ends = Internal thread
- Male Rod ends = External thread
- Weld cup for spherical bearings = A joint bearing that you weld instead of a rod end.
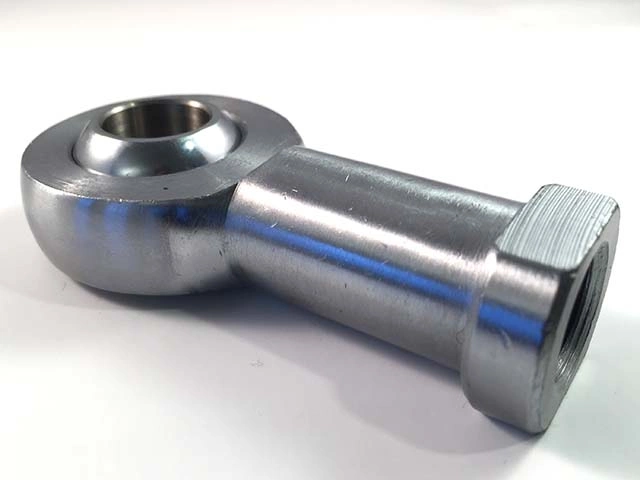
Male rod end = Male thread
The most common type of rod end / uniball. This is largely used for wheel suspension in motorsport and racing. The joint works like a bushing without any flex.
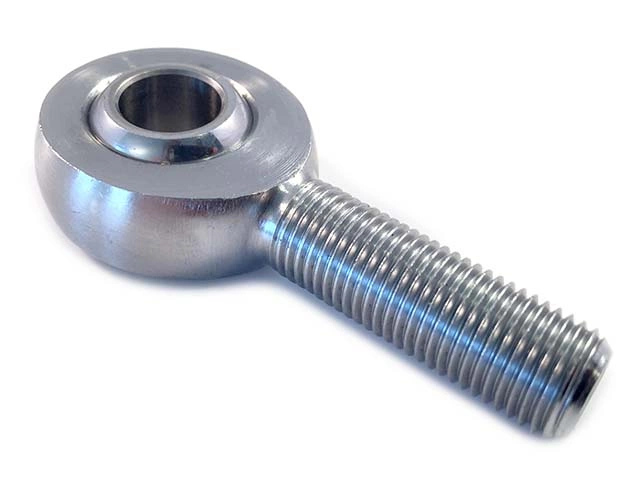

Female rod end = Female thread
These can be used together with male rod ends / uniballs but also together with a threaded rod. Be careful to use high-quality threaded rods, as most rods in a regular hardware store will not work well because of low quality.

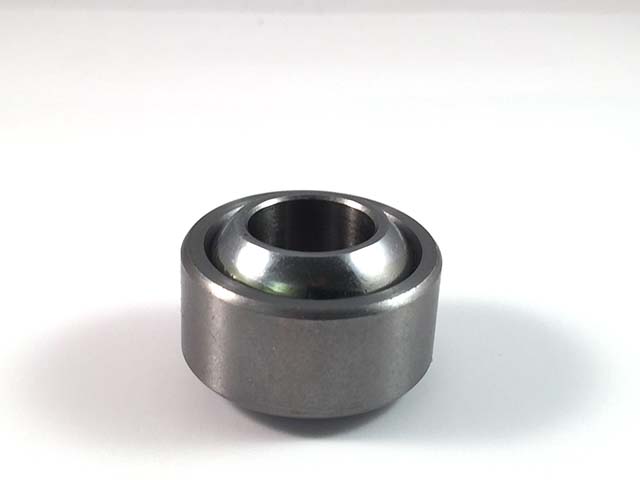
Sperical bearing = Without thread
This bearing type is mounted in a bearing cup called a weld cup. These are mounted instead of the control arm P-end at the wheel spindle.

3 ▼
Uniball size
If you decide to use rod ends, it's essential to consider the appropriate size for the intended use. A larger and stronger rod end may be necessary for a rear suspension. However, if it's for adjusting the alternator, a less strong rod end is needed as the load is lower than in a rear suspension.
Benchmark when choosing uniballs
When mounting a rod end, it should only handle axial load. Using a high-quality uniball and bolt of the same quality can help determine the weakest link, the bolt. When selecting uniballs, this can serve as a benchmark. If you anticipate reaching the limit of what the bolt or uniball can handle, it may be necessary to increase the size.
Bigger is better if you are unsure of size.
4 ▼
Material
The different materials used for uniballs depend entirely on the area in which they are to be used. Rod ends are available in the following versions:
- Chromium molybdenum for best strength and durability.
These bearings can withstand significantly more loads and shocks than the equivalent in ordinary steel. These are usually installed indoors in machinery and industry - Stainless / Acid-resistant steel
These are also installed in industry, but can also be used outdoors - Aluminum
Used for light applications that do not take shocks and as high forces as the above materials. Perfect if something is to be light and does not absorb high forces / shocks.
5 ▼
Install uniballs
To properly mount rod ends or use solutions with rod ends, it is important to select the appropriate size and thread for adjustability. Uniballs are commonly used at the end of a moving part, such as the wheel suspension in a car. It is crucial to allow the chassis control arms to work within their designated range of motion.
The bearing can move about 12-16 degrees when mounted in one direction. However, when mounted turned 90 degrees, it can move a full 360 degrees. It is important to remember this during installation to prevent the uniball from hitting its end position and breaking. When more than 12-16 degrees of movement are required, spacers can be used to achieve extra mobility, which is especially important in a wheel suspension.
If mounting the rod end on a pipe, a welding bracket should be welded on the pipe, and then a rod end with an external thread can be assembled with a lock nut.
Note that a uniball mounted at an angle in its zeor position can bottom during suspension and then break!
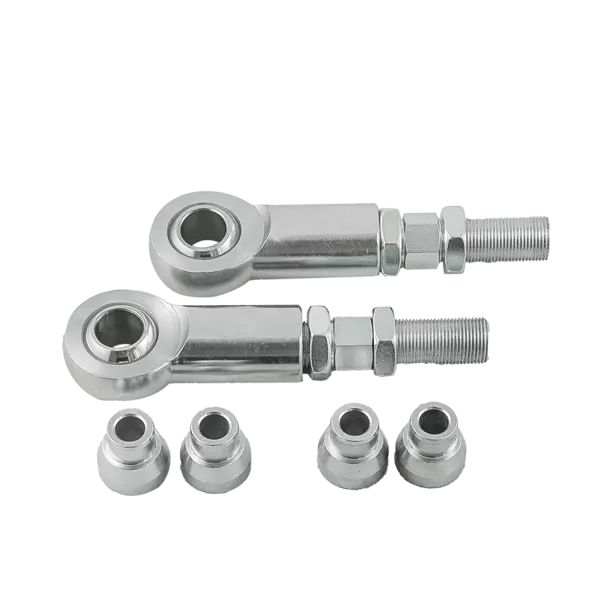
6 ▼
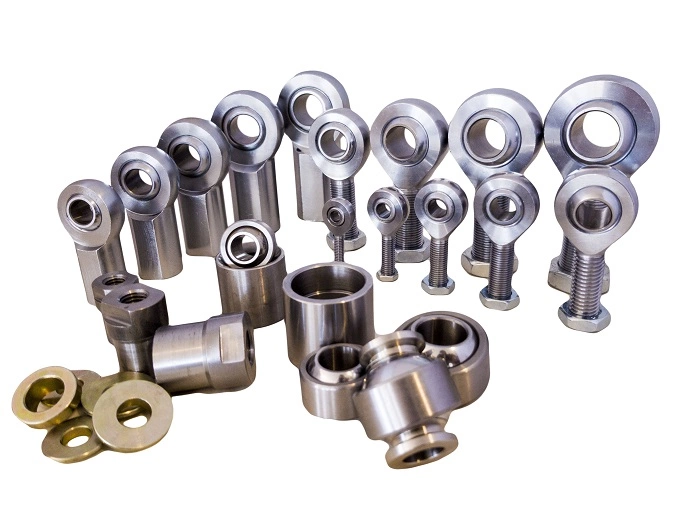
Accessories
Chassis tubing
Pipe to be used with a welding sleeve together with a rod end.
Spacers
To avoid play when you mount your rod end.
Lock nuts
To lock the rod end when you have adjusted the desired distance/length. A nut prevents the rod end from turning.
Tube adjusters
Male at one end and female at the other to easily adjust the length of the assembly without disassembling anything.
Weld on nuts
Welded onto the pipe so you can easily adjust connected rod ends at both ends.
Sealing boots
Used to protect rod ends from dirt that can damage the bearing.
Threaded tube adapters
Makes it easier to use the rod end together with pipes. Welded into the pipe to be able to mount rod ends.
Weld on brackets
To be able to easily attach rod ends to chassisand other parts.
Uniball cups
This is a spherical bearing housing that is welded onto pipes or similar.

7 ▼
Common problems
- It is important to note that the bearing should only be used within its designated work angle to avoid any potential risks of joint bearing faliure.
- Additionally, insufficient dust protection can cause dirt buildup, which can accelerate wear on the bearing surface.
- Proper geometry is also crucial, as incorrect mounting can lead to joint bearing damage.











































