Temperature sensor - Information

Here you get an overview of how a temperature sensor works and what to think about.
This type of sensor is called Temperature sensor, Temp sensor or CLT sensor (Coolant sensor)
The different categories of temperature sensors:
- Temperature sensor function
- Different types
- Choice of temp sensor
- Connections
- Temp sensor check
- Material
- Temperature sensor installation
- Accessories
- Problems
- Compare Temp sensor
1 ▼
Temperature sensor function
What is a temperature sensor?A temperature sensor detects the temperature of substances like oil, water, or intake air.
Why use a temperature sensor?
Maintaining optimal temperatures is crucial to achieving the best engine performance and durability possible. Too high or low temperatures can lead to costly breakdowns and reduced efficiency.
What function does a temperature sensor have?
The temperature sensor provides you and the control system with the engine's actual values, enabling you to optimize your machine's performance and have a clear overview of its operation.
2 ▼
Different types
PTC vs NTC type
- PTC sensor / resistor (Positive Temperature Coefficient)
Increases resistance with increasing temperature. This type is most common in the automotive world. - NTC sensor / resistor (Negative Temperature Coefficient)
Decreases resistance with increasing temperature.
Oil temperature sensor
Measures the oil temperature in your engine and can also be used to measure the gearbox oil temperature.
Water temperature sensor
Measures the temperature of the cooling water. This is an important part as oil and water directly affect each other. If one goes down, so does the other and vice versa.
Intake Temperature Sensor (IAT)
Measures intake air temperature. A high intake temperature directly affects engine power negatively.
Exhaust gas temperature
This sensor has his own page here.
For the same sensor, the resistance differs depending on whether you are measuring water or oil.
3 ▼
Choice of temp sensor
When selecting a temperature sensor, ensure that it is suitable for your intended use and compatible with your Engine management system or gauge. Many aftermarket control systems / ECU can be tailored to fit your sensor type.
4 ▼
Connections
If you are looking to install a sensor in your engine that does not fit right away, two options are available. First, you can use adapters or similar equipment to attach the sensor. Second, you can opt to weld a connection to make it fit.When installing a temperature sensor, it's important to be aware that the sensor tip may extend beyond the thread. This means that enough space should be provided in the mounting hole to accommodate it.
Please refer to the accompanying picture for a visual example.
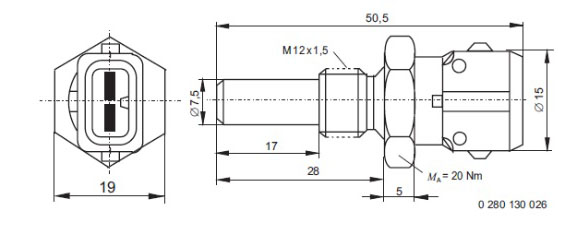
5 ▼
Temp sensor check
If the sensor is not providing a reading or giving a different value, it may be due to a problem with your application, improper contact with oil or water, or incorrect sensor installation. Therefore, ensure that the installation has been done correctly and that the sensor is suitable for the intended purpose.
To troubleshoot the issue, take the following steps:
- Verify that the sensor is properly connected to the control system or analogue meter.
- Confirm that the sensor has been mounted for the appropriate purpose.
- Manually test the sensor. If there is still no reading despite the above points being correct, the sensor is likely worn out.
6 ▼
Material
In the aftermarket in the automotive industry and racing, temperature sensors are almost exclusively made of brass with a plastic contact piece.7 ▼
Temperature sensor installation
An oil temperature sensor is usually mounted directly in the oil pan where the oil is, and this applies to both the gearbox and the engine. Some sensors are combined with pressure and temperature, which are mounted where you have the oil pressure sensor.
An intake temperature sensor (IAT) is usually mounted in the intake or pressure pipe as close to the intake as possible, before or after the throttle body.
A water temperature sensor can be mounted in the radiator and preferably as close to the outgoing channel as possible at the top of your engine in connection with the water channel.
The tightening torque for a brass sensor with M12x1.5 thread is usually 20Nm.
Please note that sensors are highly sensitive. Over-tightening sensors can result in the breakage of the sensor body and inaccurate readings.
8 ▼
Accessories
Welding connectionsTo easily mount sensors on applications where you don't have a sensor today.
Connectors
You must have the right connector for the right sensor.
9 ▼
Problems
If you notice that your car is overheating and getting too hot, it could be due to a faulty temperature sensor. This may prevent the cooling fans from starting and activating the engine management functions. Faulty sensors can cause a range of issues that can be avoided by taking the following steps:
- Mount the sensor directly onto the engine block to get the most accurate readings.
The temperature sensors are made to withstand strong engine vibrations. - Check that the sensor is correctly connected and providing a signal or value.
If not, the fault could be with the sensor, ECU, or wiring/connector. Poor contact can cause many strange issues.
▼
▼
-
Engine management / Electric
- Engine control system: The various parts available
- Ignition System Information
- Install motor control
- Pressure sensor - Information
- Temperature sensor - Information
- Buttons - Switches - Information
- Connectors - Information
- Cooling fan car - Information
- Exhaust gas temperature sensor - EGT Sensor
- Lambda sensor - Wide band lambda
- Relay - Information
- Relay box - Fuse central
- CAN protocol - Canbus
- Ethanol sensor - Information
- Gauges and Dash
- Trigger sensor information
- Dimensioning of cable [and fuse size]
- Distributor Problems (And Solution)
- How does an Ignition Coil work?











































